Skip to content
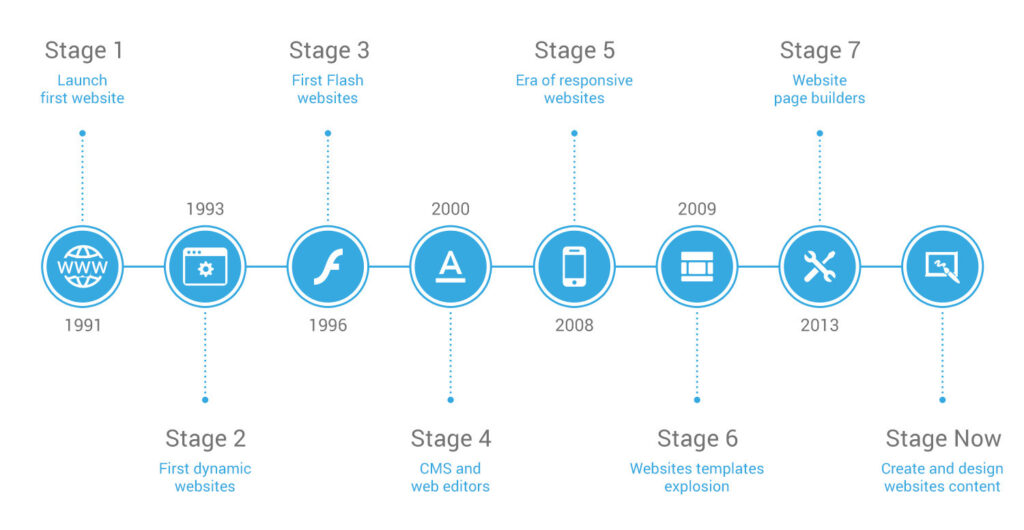
The History of Websites
1. The Beginning (1991–1995)
- The first website was created in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN.
- Early websites were plain text pages built with simple HTML.
- Web browsers like Mosaic (1993) and Netscape (1994) made the web accessible to the public.
Early Stage Websites
2. Web 1.0 — The Static Web (1995–2004)
- Websites were mostly static and informational.
- Companies began creating their first websites (Yahoo, Amazon, eBay).
- Early design techniques included frames, tables, and simple JavaScript.
The Interactive Websites
3. Web 2.0 — The Interactive Web (2004–2015)
- The web became dynamic and user-driven.
- Rise of platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter.
- Use of CSS, databases, and AJAX brought more interactivity and cleaner design.
Revolution of Websites
4. Mobile Revolution (2007–2015)
- Smartphones changed how websites were built.
- Responsive design became essential.
- CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal grew.
5. Modern Web / Web 3.0 (2015–Present)
- Websites now behave like fast, interactive applications.
- Technologies include React, Vue, Angular, and APIs.
- Builders like Elementor, Wix, and Webflow made web creation easier.
6. Today and the Future
- AI-generated websites are on the rise.
- Voice interactions, chatbots, and personalized experiences dominate.
- Growth of 3D, VR/AR web experiences.
Summary Table
| Era | Characteristics |
|---|
| 1991–1995 | Basic text, no design |
| 1995–2004 (Web 1.0) | Static, informational |
| 2004–2015 (Web 2.0) | Social, interactive |
| 2015–Now | App-like, mobile-first |
| Future | AI-driven, immersive |

